Censorship-hungry Twitter employees vented to the House Select Committee on Jan. 6 that their company wasn’t authoritarian enough when it came to curbing former President Donald Trump ahead of the 2021 Capitol riot, a newly released 122-page memo shows. “The Twitter Files,” however, prove Big Tech went out of its way to suppress the Republican president long before his ban from the platform on Jan. 8, 2021.
When the Twitter staff, or “Tweeps,” gave witness testimony to the J6 Committee last year, they likely didn’t anticipate a fact-check of their public statements against their internal communications. Then Elon Musk acquired the company in October of 2022 and released internal documents exposing Twitter’s key censorship decisions and election meddling.
Some of the material in the revelations dubbed “The Twitter Files” corroborates what these ex-staffers told the J6 Committee about Twitter’s hesitation to ban Trump until Jan. 8. Many of the uncovered documents and communications, however, prove that long before the riot, Twitter treated Trump differently than it did most world leaders.
Tweeps Agree: Big Tech Not Authoritarian Enough
Anika Navaroli, a member of Twitter’s censorship team, told the J6 Committee in anonymous testimony in July of 2022 that Twitter’s decision to delay the permanent suspension of Trump until after the riot was “absolutely indicative and emblematic of Twitter’s hands-off, willfully ignorant approach to the former President’s rhetoric on the service and on the platform.”
Much like hundreds of Twitter employees who wrote an open letter demanding the president’s permanent suspension, Navaroli claimed she lobbied for the curbing of Trump long before he was banned on Jan. 8, 2021, but her demands for action were ignored.
“For months I had been begging and anticipating and attempting to raise the reality that if nothing — if we made no intervention into what I saw occurring, people were going to die,” Navaroli said in her interview with the Democrat-dominated committee. “On Jan. 5, I realized no intervention was coming. As hard as I had tried to create one or implement one, there was nothing. We were at the whims and the mercy of a violent crowd that was locked and loaded.”
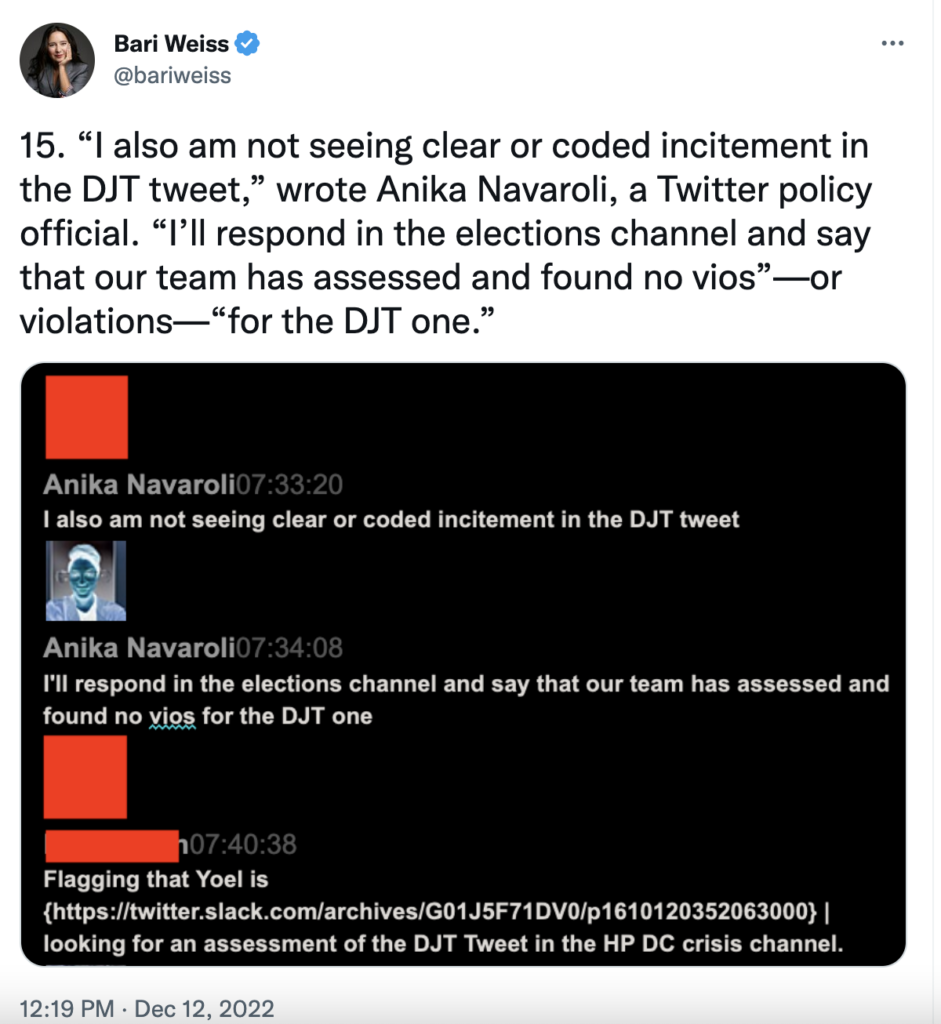
Navaroli’s frustrations furthered when, after being tasked with evaluating the validity of Trump’s online rhetoric following the Capitol riot, she ultimately dismissed the outgoing president’s tweets as above board under Twitter’s policies.
“I also am not seeing clear or coded incitement in the DJT tweet,” Navaroli wrote in a Slack chat with her colleagues on Jan. 8. “I’ll respond in the elections channel and say that our team has assessed and found no [violations] for the DJT one.”

Navaroli wasn’t alone. Another unnamed member of Twitter’s safety policy team told the J6 Committee that Twitter’s censorship teams weren’t equipped to “find a rationale to suspend the President’s account from the service, and ‘stop the insurrection’” on Jan. 6.
“The team was left to respond to rampant incitement on Twitter under its own initiative, once again without clear instruction,” the committee report states, adding later, “This understaffed, ramshackle made [one of the employees moderating content on Jan. 6] feel like she was a security guard hovering over the Capitol, trying to defend the building as the crowd tweeted out its progress during the course of the assault.”
It’s clear from these accounts that Twitter employees tried to find a cause for deplatforming Trump under the Big Tech company’s then-policies. When they failed to obtain the political results they desired, partisan Twitter executives sidestepped free speech loyalists at the company by changing the rules to target Trump alone. The Capitol riot was simply their catalyst.
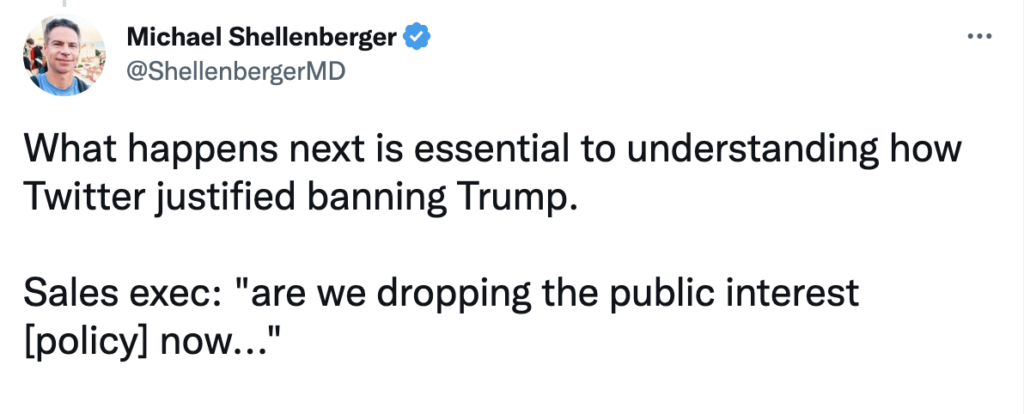
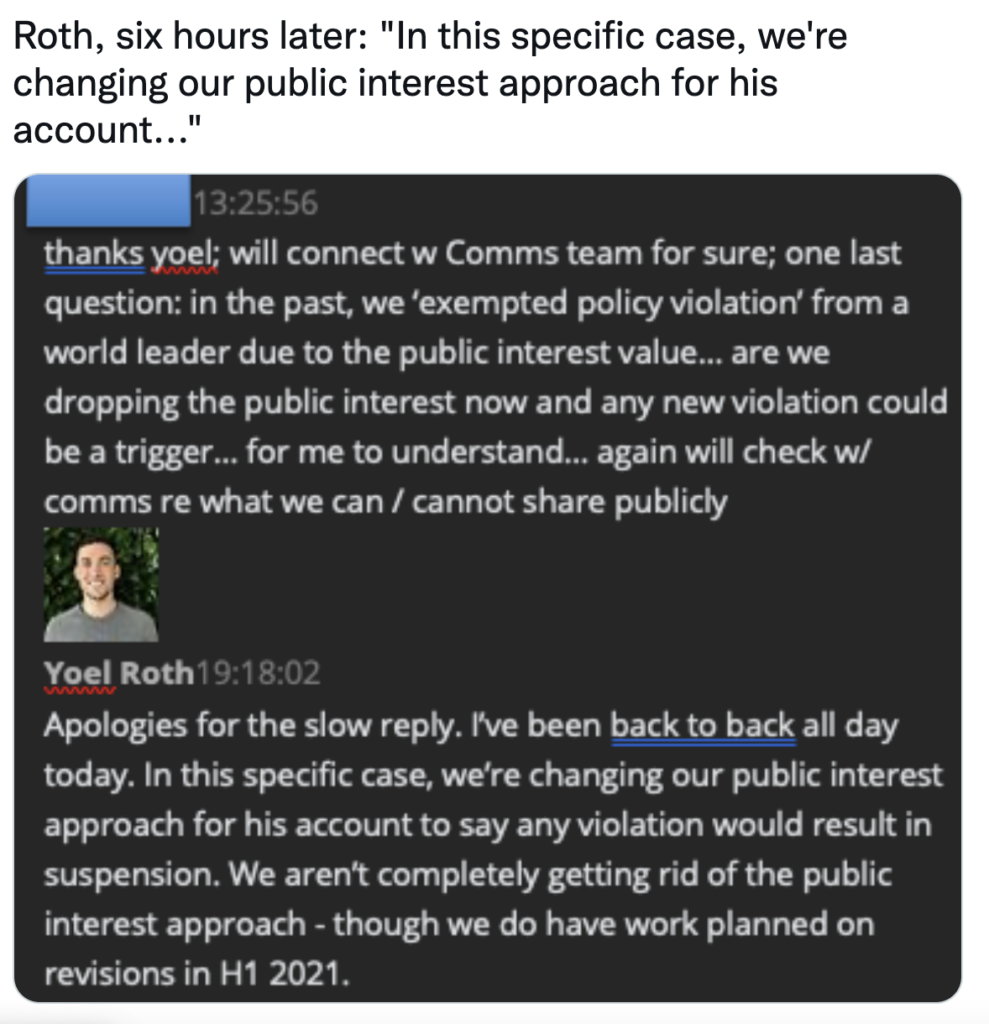
Change the Rules to Win the Game
Once Twitter executives changed the rules to remove Trump, the company and its Democrat allies celebrated.
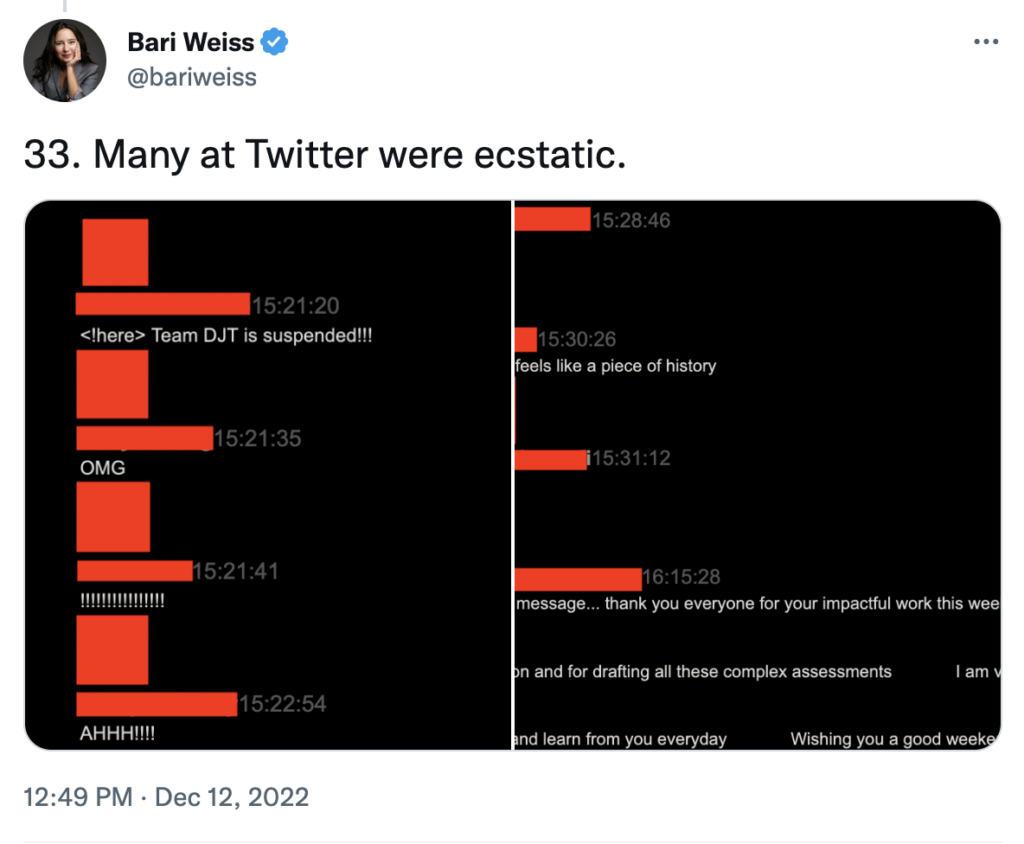
Months after Navaroli gave her testimony and Trump was barred from Twitter, members of the J6 Committee were still publicly praising her for “answering the call of the Committee and your country.”

Corporate media such as The Washington Post elevated her as “the most prominent Twitter insider known to have challenged the tech giant’s conduct toward Trump.” Business Insider amplified Navaroli with the headline, “Twitter whistleblower who foresaw the violence of Jan. 6 reveals her identity with an omen for the future of US democracy.”
Navaroli’s testimony, along with other witnesses, helped Democrats conclude that “Trump’s suspension ended the preferential treatment Twitter gave his account for years” and that Big Tech failed to prevent violence by delaying its permanent ban on Trump until after the Capitol riot.
“The former employee’s testimony confirms that Twitter saw President Trump’s potential violent incitement of his supporters as a cause for concern even prior to Election Day but chose not to take effective actions to prevent him from using the platform in this way. Moreover, this failure to act was consistent with Twitter’s longstanding deferential treatment of President Trump,” the report states.
Twitter Did Treat Trump Differently
The effort to permanently bar Trump may have concentrated around the Capitol riot and culminated with a mad scramble on Jan. 8, as Navaroli suggested. Still, as “Twitter Files” journalist Matt Taibbi noted in part three of the exposé, “the intellectual framework was laid in the months preceding the Capitol riots.”
Executives such as Twitter’s former head of trust and safety Yoel Roth, Twitter’s former legal and policy executive Vijaya Gadde, and Twitter’s recently fired general counsel and FBI veteran Jim Baker spent months building a network that could quickly respond to suppression requests and easily strike violative content and users.
“[T]he firm had a vast array of tools for manipulating visibility, most all of which were thrown at Trump (and others) pre-J6,” Taibbi noted.
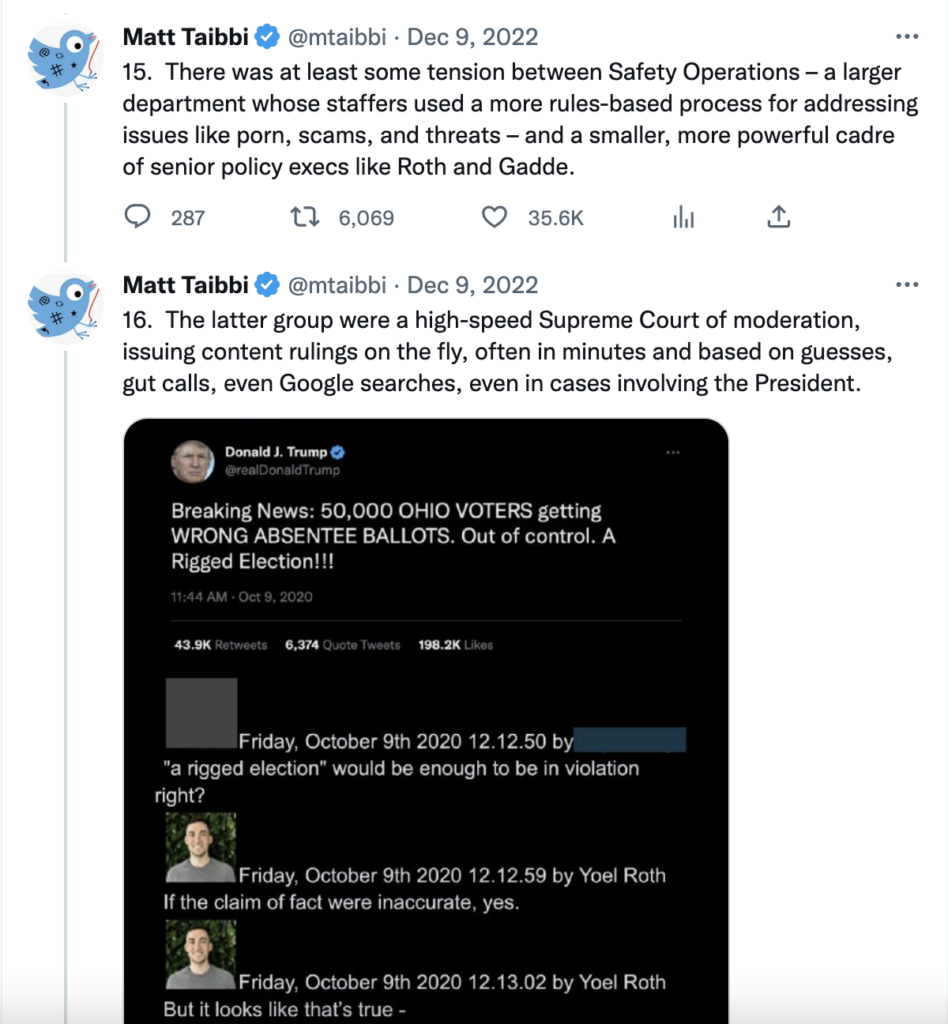
The treatment Trump received from Twitter’s top censors may have been different, but it was far from the “deferential treatment” the J6 Committee concluded had occurred.
Contrary to Tweeps’ testimonies, Trump faced several bouts of censorship including Twitter reducing the reach of his tweets, shadowbanning him, labeling his tweets with warnings, and temporarily suspending his account long before the Capitol riot.
As independent journalist Bari Weiss noted in part five of “The Twitter Files,” the Big Tech company was far more eager to justify that kind of censorship against Trump than to use it against actual dictators.
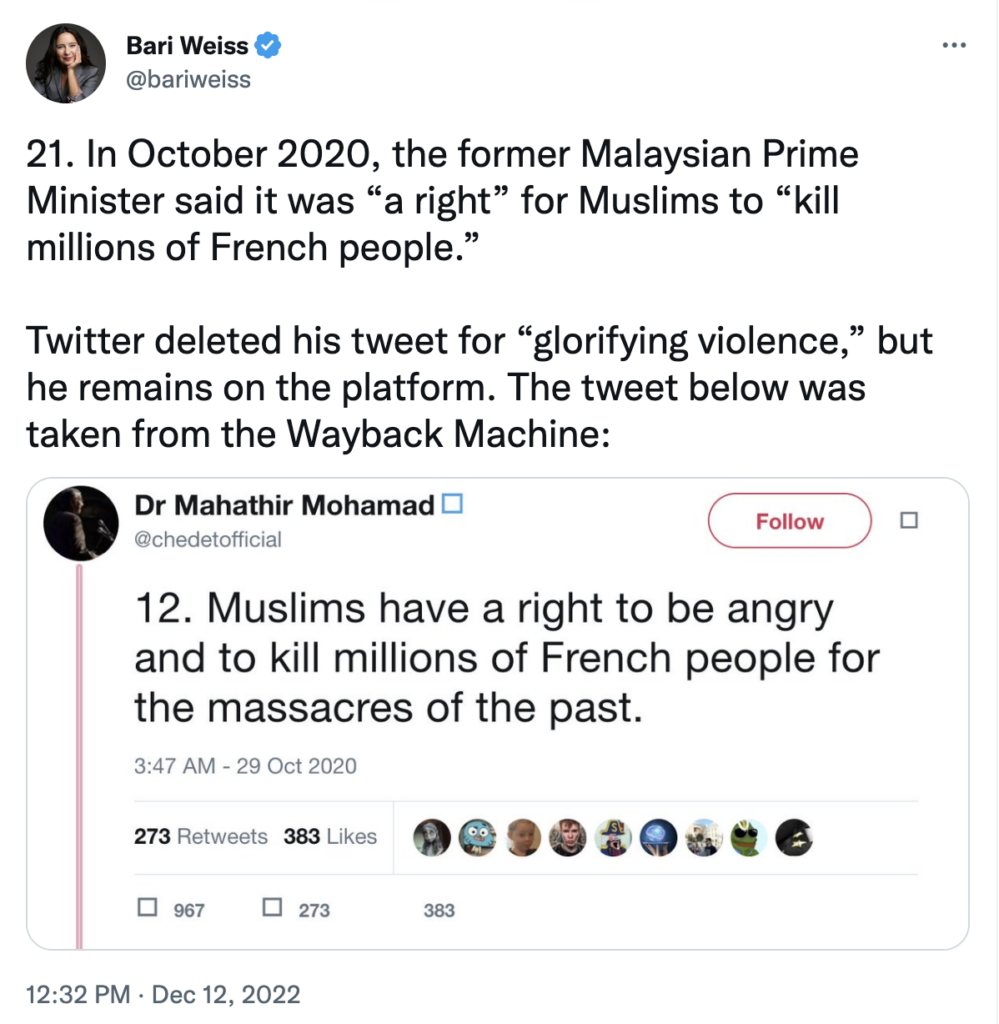
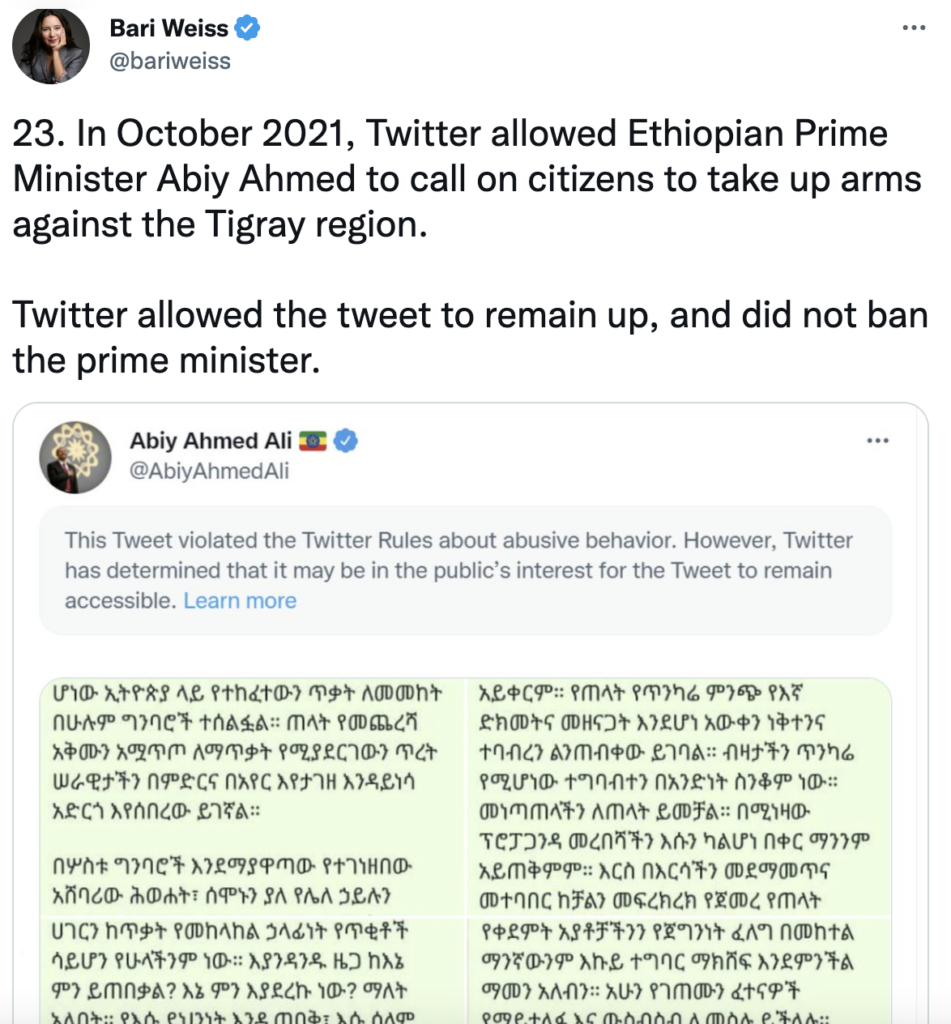
Twitter staff and executives were so overcome with their hatred for Trump that they were willing to create a reason to deplatform the president. What those employees didn’t anticipate is that their shenanigans would be blown open by “The Twitter Files” mere months after they gave sworn testimony to Democrats in Congress.
As evidenced by “The Twitter Files,” there was nothing stopping Tweeps from deplatforming Trump. In fact, Twitter, cheered by the same Democrats, worked for years to silence its political enemies at whatever cost.

